 | |
| Family | Messaging protocol |
|---|---|
| Designed by | Dave Winer, Don Box, Bob Atkinson, and Mohsen Al-Ghosein |
| First appeared | Initially as XML-RPC in June 1998 |
| Stable release | 1.2
/ 27 April 2007 |
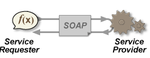
SOAP (formerly an acronym for Simple Object Access Protocol) is a messaging protocol specification for exchanging structured information in the implementation of web services in computer networks. It uses XML Information Set for its message format, and relies on application layer protocols, most often Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), although some legacy systems communicate over Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP), for message negotiation and transmission.
SOAP allows developers to invoke processes running on disparate operating systems (such as Windows, macOS, and Linux) to authenticate, authorize, and communicate using Extensible Markup Language (XML). Since Web protocols like HTTP are installed and running on all operating systems, SOAP allows clients to invoke web services and receive responses independent of language and platforms.
SOAP provides the Messaging Protocol layer of a web services protocol stack for web services. It is an XML-based protocol consisting of three parts:
SOAP has three major characteristics:
As an example of what SOAP procedures can do, an application can send a SOAP request to a server that has web services enabled—such as a real-estate price database—with the parameters for a search. The server then returns a SOAP response (an XML-formatted document with the resulting data), e.g., prices, location, features. Since the generated data comes in a standardized machine-parsable format, the requesting application can then integrate it directly.
The SOAP architecture consists of several layers of specifications for:
SOAP evolved as a successor of XML-RPC, though it borrows its transport and interaction neutrality from Web Service Addressing[2] and the envelope/header/body from elsewhere (probably from WDDX).[citation needed]
SOAP was designed as an object-access protocol and released as XML-RPC in June 1998 as part of Frontier 5.1 by Dave Winer, Don Box, Bob Atkinson, and Mohsen Al-Ghosein for Microsoft, where Atkinson and Al-Ghosein were working.[3] The specification was not made available until it was submitted to IETF 13 September 1999.[4][5] According to Don Box, this was due to politics within Microsoft.[6] Because of Microsoft's hesitation, Dave Winer shipped XML-RPC in 1998.[7]
The submitted Internet Draft did not reach RFC status and is therefore not considered a "web standard" as such. Version 1.1 of the specification was published as a W3C Note on 8 May 2000.[8] Since version 1.1 did not reach W3C Recommendation status, it can not be considered a "web standard" either. Version 1.2 of the specification, however, became a W3C recommendation on June 24, 2003.
The SOAP specification[9] was maintained by the XML Protocol Working Group[10] of the World Wide Web Consortium until the group was closed 10 July 2009. SOAP originally stood for "Simple Object Access Protocol" but version 1.2 of the standard dropped this acronym.[11]
After SOAP was first introduced, it became the underlying layer of a more complex set of web services, based on Web Services Description Language (WSDL), XML schema and Universal Description Discovery and Integration (UDDI). These different services, especially UDDI, have proved to be of far less interest, but an appreciation of them gives a complete understanding of the expected role of SOAP compared to how web services have actually evolved.
SOAP specification can be broadly defined to be consisting of the following 3 conceptual components: protocol concepts, encapsulation concepts and network concepts.[12]
The SOAP specification defines the messaging framework, which consists of:
A SOAP message is an ordinary XML document containing the following elements:
| Element | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| Envelope | Identifies the XML document as a SOAP message. | Yes |
| Header | Contains header information. | No |
| Body | Contains call and response information. | Yes |
| Fault | Provides information about errors that occurred while processing the message. | No |
Both SMTP and HTTP are valid application layer protocols used as transport for SOAP, but HTTP has gained wider acceptance as it works well with today's internet infrastructure; specifically, HTTP works well with network firewalls. SOAP may also be used over HTTPS (which is the same protocol as HTTP at the application level, but uses an encrypted transport protocol underneath) with either simple or mutual authentication; this is the advocated WS-I method to provide web service security as stated in the WS-I Basic Profile 1.1.
This is a major advantage over other distributed protocols like GIOP/IIOP or DCOM, which are normally filtered by firewalls. SOAP over AMQP is yet another possibility that some implementations support. SOAP also has an advantage over DCOM that it is unaffected by security rights configured on the machines that require knowledge of both transmitting and receiving nodes. This lets SOAP be loosely coupled in a way that is not possible with DCOM. There is also the SOAP-over-UDP OASIS standard.
XML Information Set was chosen as the standard message format because of its widespread use by major corporations and open source development efforts. Typically, XML Information Set is serialized as XML. A wide variety of freely available tools significantly eases the transition to a SOAP-based implementation. The somewhat lengthy syntax of XML can be both a benefit and a drawback. While it promotes readability for humans, facilitates error detection, and avoids interoperability problems such as byte-order (endianness), it can slow processing speed and can be cumbersome. For example, CORBA, GIOP, ICE, and DCOM use much shorter, binary message formats. On the other hand, hardware appliances are available to accelerate processing of XML messages.[16][17]Binary XML is also being explored as a means for streamlining the throughput requirements of XML. XML messages by their self-documenting nature usually have more 'overhead' (e.g., headers, nested tags, delimiters) than actual data in contrast to earlier protocols where the overhead was usually a relatively small percentage of the overall message.
In financial messaging SOAP was found to result in a 2–4 times larger message than previous protocols FIX (Financial Information Exchange) and CDR (Common Data Representation).[18]
XML Information Set does not have to be serialized in XML. For instance, CSV and JSON XML-infoset representations exist. There is also no need to specify a generic transformation framework. The concept of SOAP bindings allows for specific bindings for a specific application. The drawback is that both the senders and receivers have to support this newly defined binding.
The message below requests a stock price for AT&T (stock ticker symbol "T").
POST /InStock HTTP/1.1
Host: www.example.org
Content-Type: application/soap+xml; charset=utf-8
Content-Length: 299
SOAPAction: "http://www.w3.org/2003/05/soap-envelope"
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<soap:Envelope xmlns:soap="http://www.w3.org/2003/05/soap-envelope" xmlns:m="http://www.example.org">
<soap:Header>
</soap:Header>
<soap:Body>
<m:GetStockPrice>
<m:StockName>T</m:StockName>
</m:GetStockPrice>
</soap:Body>
</soap:Envelope>
This section needs additional citations for verification. (August 2020) |
Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP) defines a messaging envelope structure designed to carry application payload in one portion of the envelope (the message body) and control information in another (the message header).
Note: In previous versions of this specification the SOAP name was an acronym. This is no longer the case. (Underneath section 1. Introduction)
By: Wikipedia.org
Edited: 2021-06-19 11:06:13
Source: Wikipedia.org