 | |
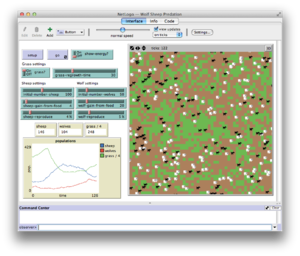 NetLogo graphical user interface | |
| Paradigms | multi-paradigm: educational, procedural, agent-based, simulation |
|---|---|
| Family | Lisp |
| Designed by | Uri Wilensky |
| Developer | Northwestern University Center for Connected Learning and Computer-Based Modeling |
| First appeared | 1999 |
| Stable release | 6.2.0
/ December 26, 2020 |
| Typing discipline | Dynamic, strong |
| Scope | Lexical |
| Implementation language | Scala, Java |
| Platform | IA-32, x86-64 |
| OS | Cross-platform: JVM |
| License | GPL |
| Filename extensions | .nlogo, .nlogo3d, .nls |
| Website | ccl |
| Influenced by | |
| Logo, StarLogo | |
NetLogo is a programming language and integrated development environment (IDE) for agent-based modeling.
NetLogo was designed by Uri Wilensky, in the spirit of the programming language Logo, to be "low threshold and no ceiling". It teaches programming concepts using agents in the form of turtles, patches, links and the observer.[1] NetLogo was designed with multiple audiences in mind, in particular: teaching children in the education community, and for domain experts without a programming background to model related phenomena.[2] Many scientific articles have been published using NetLogo.[3]
The NetLogo environment enables exploration of emergent phenomena. It comes with an extensive models library including models in a variety of domains, such as economics, biology, physics, chemistry, psychology, system dynamics.[4] NetLogo allows exploration by modifying switches, sliders, choosers, inputs, and other interface elements.[5] Beyond exploring, NetLogo allows authoring new models and modifying extant models.
NetLogo is open source and freely available from the NetLogo website.[6] It is in use in a wide variety of educational contexts from elementary school to graduate school.[7][8][9][10] Many teachers make use of NetLogo in their curricula.[11][12]
NetLogo was designed and authored by Uri Wilensky,[13] director of Northwestern University's Center for Connected Learning and Computer-Based Modeling (CCL).[14]
In addition to agent-based modeling, NetLogo also includes basic support for dynamic system modeling.
Several books have been published about NetLogo.[15]
Books available in print include:
Books available online include:
As of 2019[update], several massive open online courses are being offered that use NetLogo for assignments and/or demonstrations:
NetLogo is free and open-source software, released under a GNU General Public License (GPL).[16] Commercial licenses are also available. It is written in Scala and Java and runs on the Java virtual machine (JVM).[17] At its core is a hybrid interpreter/compiler that partially compiles user code to JVM bytecode.[18]
NetLogo Web is a version that runs on JavaScript, instead of the JVM, so models may be run in a web browser. However, it does not have all features of the desktop version, and the official website advises that the "desktop version of NetLogo is recommended for most uses".[19]
A simple multiagent model in NetLogo is the Wolf-Sheep Predation model,[20] which is shown in the screenshot above. It models the population growth of a predator/prey system over time. It has the following characteristics:
HubNet is a technology that uses NetLogo to run participatory simulations in the classroom.[21] In a participatory simulation, a whole group of users takes part in enacting the behavior of a system. Using an individual device, such as a networked computer or Texas Instruments graphing calculator, each user acts as a separate, independent agent. One example of a HubNet activity is Tragedy of the Commons,[22] which models the economic problem called the tragedy of the commons.
By: Wikipedia.org
Edited: 2021-06-18 18:14:50
Source: Wikipedia.org